Understanding Your BMR and TDEE: How Many Calories Should You Really Eat?
Read our comprehensive guide on understanding your bmr and tdee: how many calories should you really eat?.
Key Takeaways
- BMR is how many calories your body burns just to stay alive at rest, while TDEE is your total daily burn including all movement and exercise.
- Men typically have higher BMRs than women because they carry more muscle mass, and muscle tissue burns way more calories than fat.
- To lose weight eat 500 calories below your TDEE, to gain weight eat 500 calories above it, and to maintain just eat at your TDEE number.
- Your activity level multiplier ranges from 1.2 for couch potatoes up to 1.9 for people who train hard daily and work physical jobs.
- Recalculate your numbers whenever your weight, training schedule, or daily activity changes significantly so your calories stay dialed in.
Get a Free AI Coach on WhatsApp
Ask questions, get workout plans, and track your progress — all from WhatsApp.
Message Your CoachAre you looking to optimize your nutrition and wondering how many calories you should really eat? Understanding your Basal Metabolic Rate (BMR) and Total Daily Energy Expenditure (TDEE) is the key to achieving your health goals. In this comprehensive guide, we'll delve into the concepts of BMR and TDEE and how to use them to tailor your diet effectively.
What is Basal Metabolic Rate (BMR)?
Your Basal Metabolic Rate (BMR) represents the number of calories your body needs to maintain basic physiological functions at rest, such as breathing, circulation, and cell production. Essentially, it’s the energy your body requires to keep you alive.
Several factors influence your BMR, including:
- •Age: Younger people generally have a higher BMR.
- •Gender: Men typically have a higher BMR due to more muscle mass.
- •Body composition: Muscle burns more calories than fat, so individuals with more muscle mass have a higher BMR.
- •Genetics: Your genes can impact your BMR.
To calculate your BMR, you can use the Harris-Benedict equation, which considers your weight, height, age, and gender. For example:
For men: BMR = 88.362 + (13.397 x weight in kg) + (4.799 x height in cm) - (5.677 x age in years)
For women: BMR = 447.593 + (9.247 x weight in kg) + (3.098 x height in cm) - (4.330 x age in years)
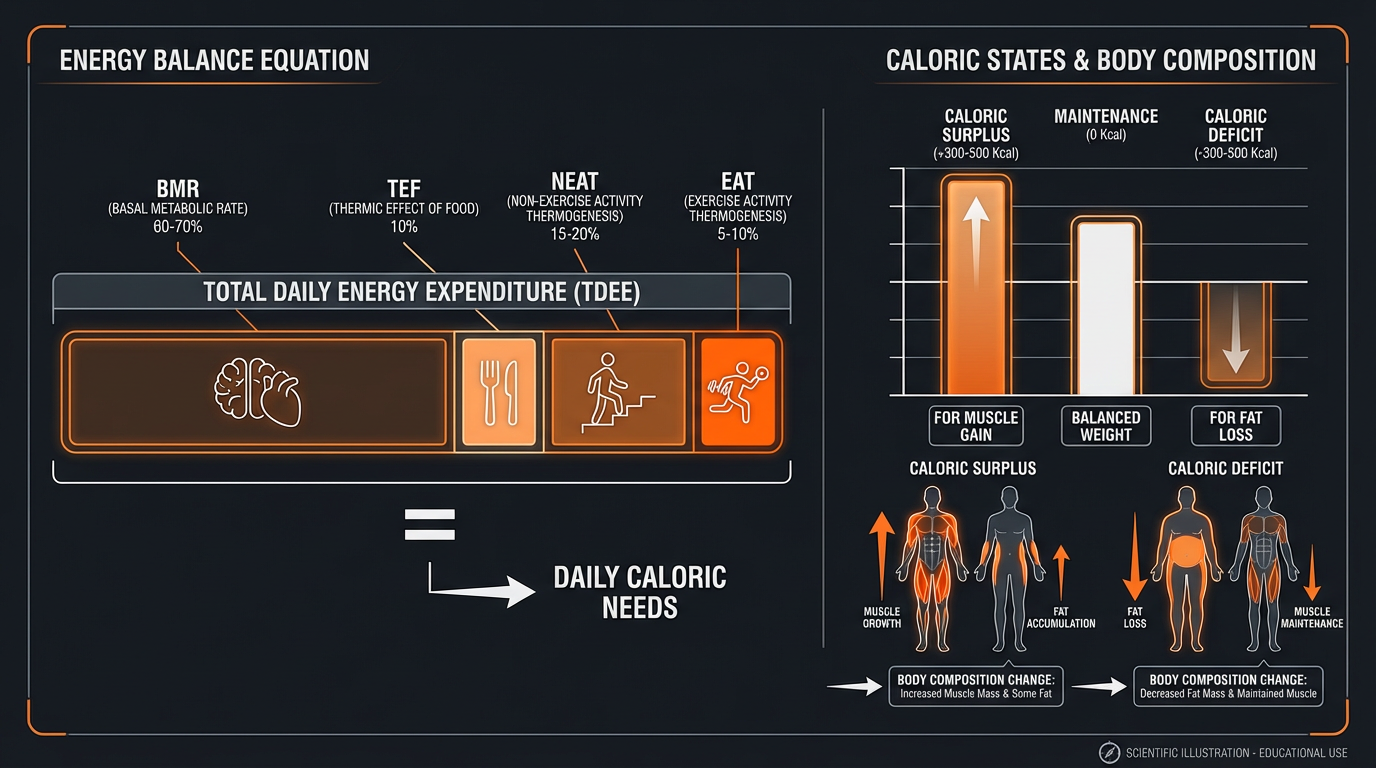
Understanding Total Daily Energy Expenditure (TDEE)
Your Total Daily Energy Expenditure (TDEE) is the total number of calories you burn in a day, taking into account all activities, from sleeping and eating to exercising and working. It combines your BMR with the calories burned through physical activities and other bodily functions.
Calculating your TDEE involves multiplying your BMR by an activity factor:
- •Sedentary (little or no exercise): TDEE = BMR x 1.2
- •Lightly active (light exercise/sports 1-3 days/week): TDEE = BMR x 1.375
- •Moderately active (moderate exercise/sports 3-5 days/week): TDEE = BMR x 1.55
- •Very active (hard exercise/sports 6-7 days a week): TDEE = BMR x 1.725
- •Super active (very hard exercise/physical job): TDEE = BMR x 1.9
For example, if your BMR is 1,600 calories and you lead a moderately active lifestyle, your TDEE would be 1,600 x 1.55 = 2,480 calories. This means you need to consume around 2,480 calories to maintain your current weight.
How to Use BMR and TDEE for Your Goals
Now that you understand what BMR and TDEE are, it's time to apply this knowledge to achieve your personal goals.
Weight Loss
If you aim to lose weight, create a calorie deficit by consuming fewer calories than your TDEE. A safe and sustainable calorie deficit is typically around 500 calories per day, translating to about 1 pound of weight loss per week. For a TDEE of 2,480 calories, you’d aim to consume approximately 1,980 calories daily.
Weight Gain
To gain weight, you need to consume more calories than your TDEE. A surplus of 500 calories per day can help you gain about 1 pound per week. So, for a TDEE of 2,480 calories, you should aim to consume around 2,980 calories daily.
For muscle gain, combine a calorie surplus with strength training. Protein intake is crucial, typically around 1.2 to 2.2 grams per kilogram of body weight.
Maintaining Weight
If you’re looking to maintain your weight, consuming calories equal to your TDEE is key. Monitor your lifestyle and activity levels, making adjustments as necessary to ensure your calorie intake aligns with your energy expenditure.
Common Questions about BMR and TDEE
Many people wonder how often they should recalculate their BMR and TDEE. It's advisable to do so whenever there are significant changes in your weight, activity level, or lifestyle. This ensures your calorie intake remains aligned with your energy needs.
Another common concern is whether you should eat back calories burned through exercise. While it's not absolutely necessary, doing so can help maintain consistent energy levels, particularly during intense or prolonged physical activity.
Conclusion
Understanding your BMR and TDEE is a powerful tool in managing your diet and achieving your health goals. By calculating these values, you can make informed decisions about your calorie intake, whether your goal is to lose weight, gain muscle, or maintain your current weight. Remember, it's essential to adjust your calculations as your body and activity levels change over time.
Ready to take control of your diet and health? Start by calculating your BMR and TDEE today! If you have any questions or need personalized advice, don’t hesitate to reach out to a nutritionist or dietitian. Your journey to a healthier you begins now!
Frequently Asked Questions
- What's the difference between BMR and TDEE?
- BMR is the calories your body burns just to stay alive (breathing, heartbeat, organ function). TDEE is your total daily burn including exercise and daily activity. You should eat based on your TDEE, not your BMR — eating at BMR will leave you underfueled.
- How do I calculate how many calories I should eat?
- Multiply your bodyweight in pounds by 14-16 for a rough maintenance estimate (14 if you're sedentary, 16 if you're active). Track your weight for 2 weeks — if it's stable, that's your actual TDEE. Then adjust up or down based on your goal.
- Are online TDEE calculators accurate?
- They're a starting point, not gospel. Most are off by 10-20% because they can't account for your individual metabolism, NEAT levels, and activity quality. Use a calculator to get a starting number, then adjust based on real-world results over 2-3 weeks.
- Should I eat back the calories I burn exercising?
- Not all of them. Fitness trackers massively overestimate calorie burn — often by 30-50%. If your tracker says you burned 500 calories, you probably burned 250-350. Set your calories based on your weekly average weight trend, not daily exercise estimates.